College Station Cat Clinic
1010 College Ave.Wheaton, IL 60187(630)690-4949
www.collegestationcat.com
Cat Cavities
 |
Cat cavities that are not cavities
Feline tooth resorption is a common and painful condition in cats caused by the erosion of tooth enamel. Studies have shown over 65-85% of cats over the age of 5 are affected by tooth resorption. The most common teeth affected are the lower premolars. These lesions were originally called “cat cavities”. We know they are not caused by bacteria like human cavities and therefore “cat cavities” is an incorrect term. Currently the cause is unknown , but genetics seem to play a role.
Tooth resorption appears as gum tissue growing into the tooth or covering the base of the tooth. Often teeth undergoing resorption will only be detected by dental radiographs (x-rays) as two thirds of cat’s teeth are under the gums and are not viewable. Studies have shown that without dental radiographs, significant pathology is missed in up to 75% of pets.
|

Cats and pain
Cats hide pain, therefore outwards signs of pain may be subtle. Owners typically fail to realize their cat is painful until after they experience positive behavioral changes after treatment. The best and only treatment for tooth resorption is extraction. Dental radiographs are essential for diagnosing and treating these lesions. Our goal is to identify and treat all lesions under one anesthetic period and restore your cat’s oral health.
|
 |

|
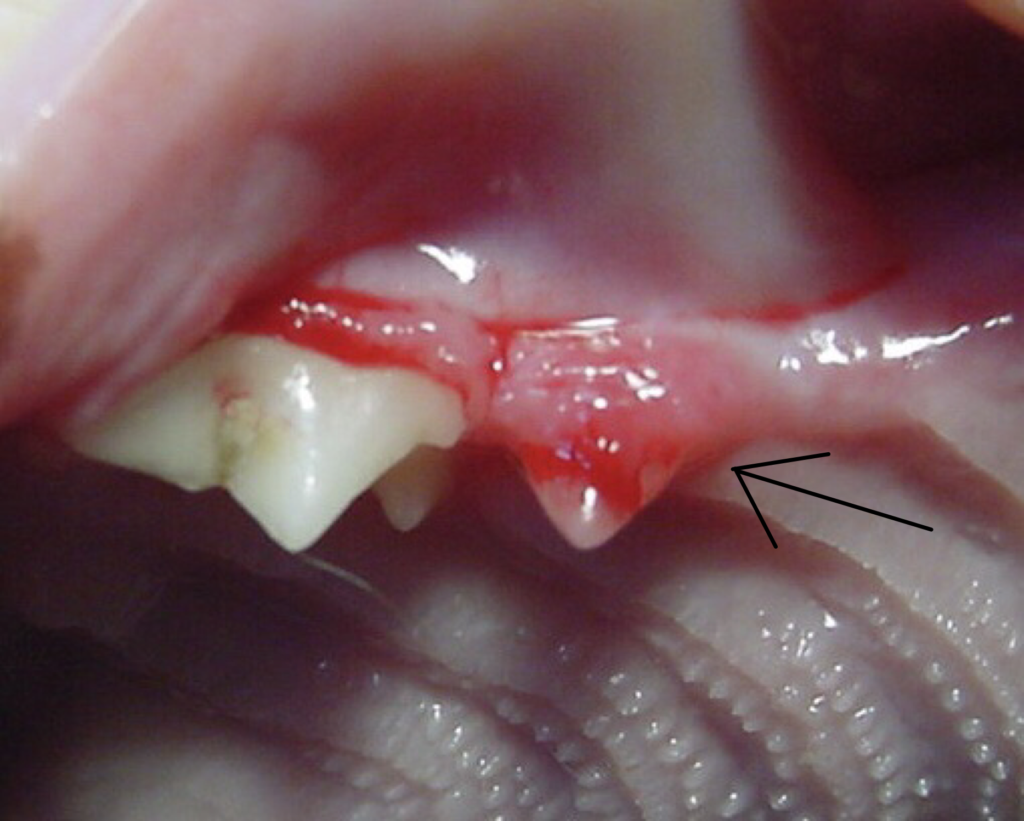
What resorption lesions look like to our eyes
Tooth resorption appears as gum tissue growing into the tooth or covering the base of the tooth. Some teeth undergoing tooth resorption are not clinically apparent until dental x-rays are taken.
|
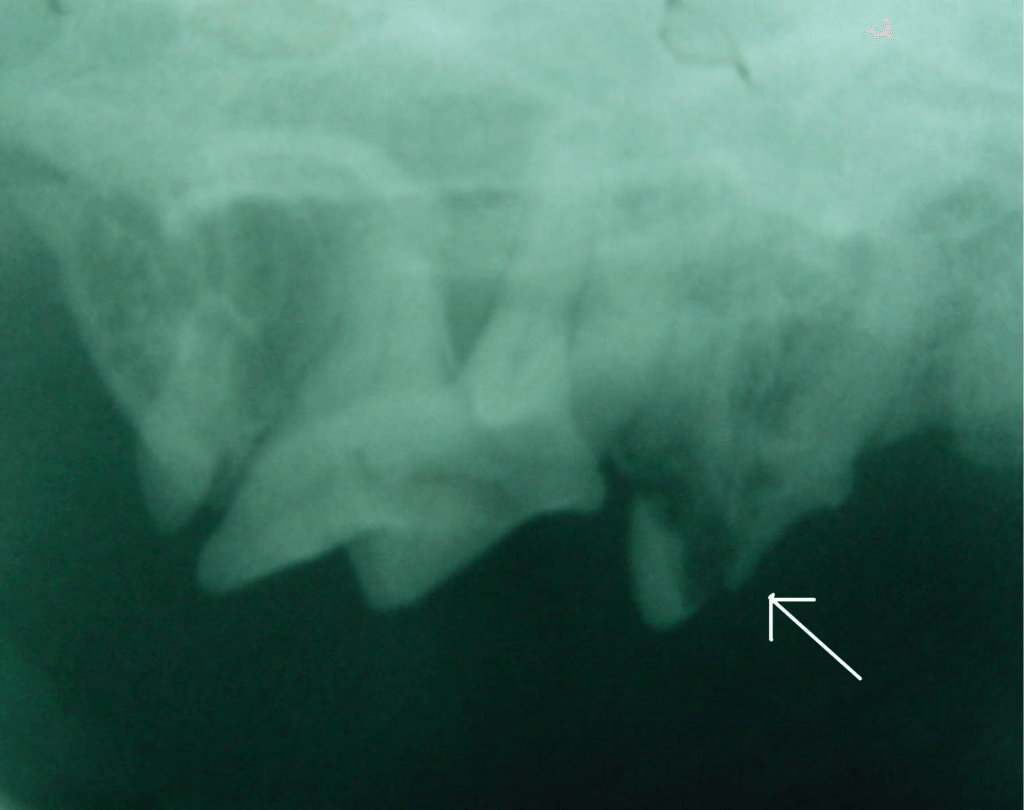
What resorption lesions look like on X-rays
The resorptive lesions appear as a loss of mineral or enamel of tooth. Resorptive lesions appear to be a ” black hole in the white tooth”. Is is impossible to see resorptive lesion below the gums without dental x-rays.
|
|